- Product Description and Classification
- Mandatory Requirements
- What are the Requirements for the Niche Markets?
- Which Quality Support Organizations in Lebanon Can Help Me?
Product Description and Classification
Sauces and pastes mainly consist of a combination of ingredients to form a harmonious taste. A sauce changes a dish by adding flavors, texture, viscosity and moistness to food. It can be based on (or include) a variety of ingredients such as the juice of fruits and vegetables, vegetable oil, herbs, wine, aromatics, dairy, honey, vinegar, nuts and molasses.The sauce can balance the flavors between salt, bitter, sweet, sour and umami, depending on the dish that is being prepared. The sauces can also differ based on the texture and consistency ranging from thin sauces to thickened sauces.
Sauces include ready-to-eat sauces, gravies, and dressings, and mixes to be reconstituted before consumption. The ready-to-eat products are divided into subcategories for emulsified and non-emulsified products, whereas the mixes are divided into subcategories that encompass both emulsified and non-emulsified sauce mixes:
- Emulsified sauces and dips (e.g., mayonnaise, salad dressing, onion dips), such as sauces, gravies, dressing-based sauces and dips, at least in part, in a fat- or oil-in-water emulsion—examples include salad dressing (e.g., French, Italian, Greek, ranch style), fat-based sandwich spreads (e.g., mayonnaise with mustard), salad cream, and fatty sauces and snack dips (e.g., bacon and cheddar dip, onion dip).
- Non-emulsified sauces (e.g., ketchup, cheese sauce, cream sauce, brown gravy) include water, coconut milk, and milk-based sauces, gravies, and dressings, such as barbecue (BBQ) sauce, tomato ketchup, cheese sauce, Worcestershire sauce, Asian thick Worcestershire sauce (tonkatsu sauce), chili sauce, sweet and sour sauce, and white sauce (milk-based sauce, with little added fat and flour)
- Mixes for sauces and gravies are concentrated products, usually in powdered form, to be mixed with water, milk, oil, or other liquid to prepare a finished sauce or gravy, including mixes for cheese sauce, hollandaise sauce, and salad dressing (e.g., Italian or ranch dressing) Clear sauces (e.g., fish sauce) include thin, non-emulsified clear sauces that may be water based and used as condiments or ingredients rather than as finished gravy. Examples include oyster sauce and Thai fish sauce (nam pla).
Combined Nomenclature Number Product 210310 Soya sauce 210320 Tomato Ketchup and other tomato sauces 210330 Mustard flour and meal and prepared mustard 210390 Other
Mandatory Requirements
General Guidelines
- Lebanese companies should verify whether the U.S. government has prohibited doing business with a particular Lebanese company/ individual due to past export control violations or because they are subject to a U.S. sanctions program.
- Lebanese companies should consult the BIS Denied Persons List and the Treasury Department Office of Foreign Assets Control’s (OFAC) Specially Designated Nationals and Blocked Persons Lists provided in the sites below.
- The International Trade Administration’s Consolidated Screening List combines export-screening databases from the Departments of Commerce, State, and the Treasury into a single search tool. U.S. exporters may conduct electronic screens of potential international export partners using this database. - For a number of items, specific export licenses are required. These items include products whose high-tech nature implies that export may involve a national security risk. Contacting BIS will enable an exporter to determine whether a specific item requires a license. If a specific license is required, one of the considerations is the reliability of the end-user. Government agencies and companies with a solid business reputation are more likely to be granted a license.
- Lebanese companies should consult the BIS Denied Persons List and the Treasury Department Office of Foreign Assets Control’s (OFAC) Specially Designated Nationals and Blocked Persons Lists provided in the sites below.
- The International Trade Administration’s Consolidated Screening List combines export-screening databases from the Departments of Commerce, State, and the Treasury into a single search tool. U.S. exporters may conduct electronic screens of potential international export partners using this database. - For a number of items, specific export licenses are required. These items include products whose high-tech nature implies that export may involve a national security risk. Contacting BIS will enable an exporter to determine whether a specific item requires a license. If a specific license is required, one of the considerations is the reliability of the end-user. Government agencies and companies with a solid business reputation are more likely to be granted a license.
Quality Requirements
Further to the mentioned above, all companies interested in exporting sauces to the United States of America should consider the following additional steps:
1- Register Your Facility with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration:
According to the FDA website any importer can import their food products into the United States without prior sanction of the FDA if the facility is registered and they give prior notice to the FDA of food shipments. You can register your facility on the FDA website.
2- Designate a U.S. Food Agent to handle your U.S. Communications:
All importers of food under U.S. requirements must have a U.S. food agent to act as a liaison for FDA communications regarding incoming food shipments. The FDA will communicate with your agent to schedule inspections and to verify that all food safety requirements are being upheld. This particular step is of the utmost importance. While it may seem simple to designate your importer or even your customs broker as your agent, the FDA recommends using a stateside agent and even offers a company directly through the FDA website, which can act as your agent. Usually the State Agent service includes:
1- Register Your Facility with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration:
According to the FDA website any importer can import their food products into the United States without prior sanction of the FDA if the facility is registered and they give prior notice to the FDA of food shipments. You can register your facility on the FDA website.
2- Designate a U.S. Food Agent to handle your U.S. Communications:
All importers of food under U.S. requirements must have a U.S. food agent to act as a liaison for FDA communications regarding incoming food shipments. The FDA will communicate with your agent to schedule inspections and to verify that all food safety requirements are being upheld. This particular step is of the utmost importance. While it may seem simple to designate your importer or even your customs broker as your agent, the FDA recommends using a stateside agent and even offers a company directly through the FDA website, which can act as your agent. Usually the State Agent service includes:
- Registration Renewal: Mandatory Biennial FDA-Food Facility Registration Renewal
- Certificate of Registration: Certificates issued by Registrar Corp provide confirmation of your facility’s registration to industry
- Registration Updates: Registrations must be updated within 60 days of a change in required information
- Detention Assistance: Communication with FDA on your behalf to seek the release of a detained shipment
- Mock FDA Inspection: Onsite expert assistance.
- DUNS Assistance: Obtain a DUNS number or update an existing DUNS record
- FDA Compliance Monitoring: A unique system that continuously monitors your company’s FDA compliance status
Tips
- Consult the file below to identify your suitable agent, depending on the location as well as the type of product want to export to the United States of America
Obtain all Required Permits
- According to the U.S. Customs and Border Protection, food products that are imported into the United States may require additional permits, health certificates and/or other specialized certifications. These foods include but are not limited to: meat, milk, poultry, eggs, and other products that are from animal origin.
- The U.S. Customs and Border Protection assigns an Import Specialist at each port of entry that you may consult with regarding the requirements for your particular food product. They also highly recommend hiring a customs broker that can assist with your CBP entry.
- Food products must have a PN (Prior Notice) filed with the FDA to alert them of the shipment of your product for receipt at the port of entry. Once your food shipment(s) is received, it will be subjected to a thorough inspection to pass all food safety requirements. These inspections can be detailed to you by the Import Specialist so that you can ensure your imported food products will be readily received and will not be detained for not passing inspection.
N.B A Prior notice is a mandatory notification to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) of imported shipments of articles of food prior to their arrival in the United States. The notice holds information about the product, quantity, and packaging, and related facilities, such as the manufacturer, shipper, owner, and ultimate consignee.
Prior Notice Form:
4- Understand the FDA Requirements for Your Food Product
Each food shipment being imported into the United States, from fresh fruit to livestock, has particular requirements that must be met to pass inspection and be permitted to pass through the port of entry.
For further questions regarding the FDA regulations regarding your food product here is a list of helpful links that can direct you to the department that handles your particular item:
- Plant and Animal Items - U.S. Department of Agriculture: www.usda.gov
- Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service:
https://www.aphis.usda.gov/aphis/ourfocus/planthealth/import-information
- The U.S. Customs and Border Protection assigns an Import Specialist at each port of entry that you may consult with regarding the requirements for your particular food product. They also highly recommend hiring a customs broker that can assist with your CBP entry.
- Food products must have a PN (Prior Notice) filed with the FDA to alert them of the shipment of your product for receipt at the port of entry. Once your food shipment(s) is received, it will be subjected to a thorough inspection to pass all food safety requirements. These inspections can be detailed to you by the Import Specialist so that you can ensure your imported food products will be readily received and will not be detained for not passing inspection.
N.B A Prior notice is a mandatory notification to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) of imported shipments of articles of food prior to their arrival in the United States. The notice holds information about the product, quantity, and packaging, and related facilities, such as the manufacturer, shipper, owner, and ultimate consignee.
Prior Notice Form:
4- Understand the FDA Requirements for Your Food Product
Each food shipment being imported into the United States, from fresh fruit to livestock, has particular requirements that must be met to pass inspection and be permitted to pass through the port of entry.
For further questions regarding the FDA regulations regarding your food product here is a list of helpful links that can direct you to the department that handles your particular item:
- Plant and Animal Items - U.S. Department of Agriculture: www.usda.gov
- Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service:
https://www.aphis.usda.gov/aphis/ourfocus/planthealth/import-information

Tips
- Lebanon's export of Soya Sauce (210310) to United States of America https://globaltradehelpdesk.org/en/export-210310-from-lb-to-us/assess-requirements/regulations/product-requirements
- Lebanon's export of Tomato Ketchup and other Tomato Sauces (210320) to United States of America https://globaltradehelpdesk.org/en/export-210320-from-lb-to-us/assess-requirements/regulations
- Lebanon's export of Mustard Flour and Meal, Whether or not Prepared , and Mustard (210330) to United States of America https://globaltradehelpdesk.org/en/export-210330-from-lb-to-us/assess-requirements/regulations
- Lebanon's export of Preparations for sauces and prepared sauces; mixed condiments and seasonings (excluding soya sauce, tomato ketchup and other tomato sauces, mustard, and mustard flour and meal) (210390) to United States of America https://globaltradehelpdesk.org/en/export-210390-from-lb-to-us/assess-requirements/regulations
Packaging and Labelling
Consumers are being more interested in their health which is directly related to their food consumption. Therefore, it’s of high importance to focus on transparency and visibility when stating the nutritional information, including calories, sugar, fat and other ingredients on the packaged food . A recent Mintel Survey has highlighted the following trends:
- 63% of consumers worldwide are increasingly trying to include plant ingredients in their diet.
- 1 out of 3 condiment consumers in the U.S. aged 16 to 24 stated that they prefer organic ingredients.
- 35% of sauce and/or marinade consumers in the U.S. are chasing healthier choices.
- 58% of U.S. consumers eating plant-based proteins more often declare that it is healthier than consuming meat.
Make Sure Your Product is Labeled Appropriately
According to the FDA, food items that are canned, packaged, baked goods or seafood must be labeled with the appropriate information. This information includes but is not limited to: country of origin, nutrition information and ingredient information. Depending on the size of your product and product packaging, the FDA has issued multiple formats that are permissible for use for labeling.
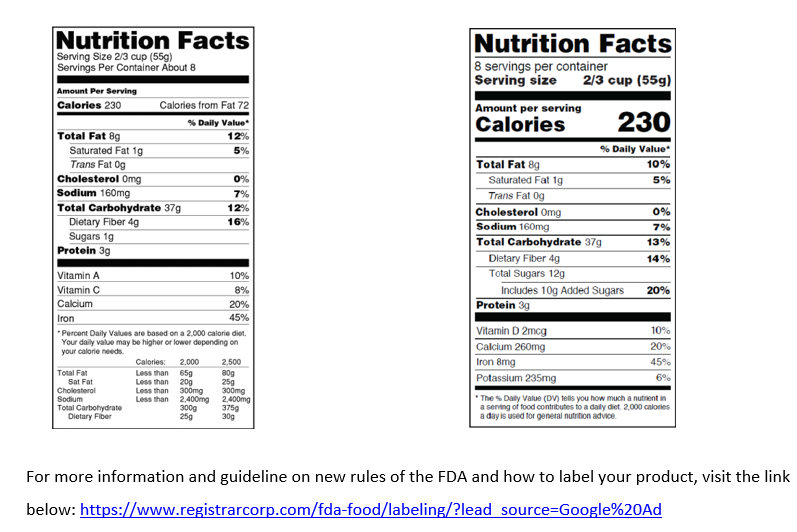
Businesses that average over $10 million in annual sales were required to make their nutrition facts labels comply with new U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) labeling rules by January 1, 2020.As of January 1, 2021, all other food businesses are required to update their labels. FDA’s new rules mandate significant changes to the Nutrition Facts Chart format, serving sizes, daily values, and more. For more information and guideline on new rules of the FDA and how to label your product, visit the link below: https://www.registrarcorp.com/fda-food/labeling/?lead_source=Google%20Ad
- 63% of consumers worldwide are increasingly trying to include plant ingredients in their diet.
- 1 out of 3 condiment consumers in the U.S. aged 16 to 24 stated that they prefer organic ingredients.
- 35% of sauce and/or marinade consumers in the U.S. are chasing healthier choices.
- 58% of U.S. consumers eating plant-based proteins more often declare that it is healthier than consuming meat.
Make Sure Your Product is Labeled Appropriately
According to the FDA, food items that are canned, packaged, baked goods or seafood must be labeled with the appropriate information. This information includes but is not limited to: country of origin, nutrition information and ingredient information. Depending on the size of your product and product packaging, the FDA has issued multiple formats that are permissible for use for labeling.
Businesses that average over $10 million in annual sales were required to make their nutrition facts labels comply with new U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) labeling rules by January 1, 2020.As of January 1, 2021, all other food businesses are required to update their labels. FDA’s new rules mandate significant changes to the Nutrition Facts Chart format, serving sizes, daily values, and more. For more information and guideline on new rules of the FDA and how to label your product, visit the link below: https://www.registrarcorp.com/fda-food/labeling/?lead_source=Google%20Ad

Tips
- When accessing the U.S. market, it’s important to follow the new food diets and target these health trends when promoting, packaging and labelling your product in order to gain attention:
- There are arising trends in the U.S. food consumption including focusing on sugar intake, prioritizing plant-based food, and placing their good health as a top priority.
- Low-carb and Keto diets are thriving, while driving innovation in sweetened food and eliminating carbohydrates. ity.
- For food ingredients and packaging which is regulated by the FDA, check the following link https://www.fda.gov/food/food-ingredients-packaging
What are the Requirements for the Niche Markets?
Organic Certification
In the US, the FDA does not regulate the use of the term “organic” on food labels. The USDA requirements for products that are labeled with the term "organic" are separate from the laws that the FDA enforces. Moreover, food products that are ordinarily under the FDA's jurisdiction and that are labeled with organic claims must comply with both the USDA NOP regulations for the organic claim and the FDA regulations for food labeling and safety.
The National Organic Program (NOP), part of USDA’s Agricultural Marketing Service (AMS), establishes international organic import and export policies to facilitate trade and to expand market opportunities for certified organic farms and businesses around the world.
Imported organic products must be certified to one of the following standards to be sold in the U.S.:
Certifiers are responsible for making sure that the USDA organic products meet all organic standards. There are five basic steps to organic certification:
1. The farm or business adopts organic practices, selects a USDA-accredited certifying agent, and submits an application and fees to the certifying agent.
2. The certifying agent reviews the application to verify that the practices comply with the USDA organic regulations.
3. An inspector conducts an on-site inspection of the applicant’s operation.
4. The certifying agent reviews the application and the inspector’s report to determine if the applicant complies with the USDA organic regulations.
5. The certifying agent issues an organic certificate. To maintain organic certification, your certified organic farm or business will go through an annual review and inspection process. If your operation is not located in the U.S., see our International Trade page to learn more about your options for organic certification
The National Organic Program (NOP), part of USDA’s Agricultural Marketing Service (AMS), establishes international organic import and export policies to facilitate trade and to expand market opportunities for certified organic farms and businesses around the world.
Imported organic products must be certified to one of the following standards to be sold in the U.S.:
- The USDA organic regulations — USDA authorizes organizations around the world to certify farms and businesses to the USDA organic regulations.
- An authorized international standard — the U.S. has established trade partnerships with international countries.
Certifiers are responsible for making sure that the USDA organic products meet all organic standards. There are five basic steps to organic certification:
1. The farm or business adopts organic practices, selects a USDA-accredited certifying agent, and submits an application and fees to the certifying agent.
2. The certifying agent reviews the application to verify that the practices comply with the USDA organic regulations.
3. An inspector conducts an on-site inspection of the applicant’s operation.
4. The certifying agent reviews the application and the inspector’s report to determine if the applicant complies with the USDA organic regulations.
5. The certifying agent issues an organic certificate. To maintain organic certification, your certified organic farm or business will go through an annual review and inspection process. If your operation is not located in the U.S., see our International Trade page to learn more about your options for organic certification


Tips
- People who sell or label a product "organic" when they know it does not meet the USDA standards can be assessed a financial penalty with fines of several thousands of dollars for each violation
- In order to certify your product, you’ll need to access the list of certifier agents in the US For organic certifier agent check
- For organic rules and regulations check https://www.ams.usda.gov/rules-regulations/organic
- The USDA currently has organic equivalence with the following governments: Canada, European Union, Japan, Korea, Switzerland, Taiwan, and United Kingdom
Gluten-free Certification
On August 2, 2013, FDA issued a final rule defining “gluten-free” for food labeling, which is helping consumers, especially those living with celiac disease, be confident that items labeled “gluten-free” meet a defined standard for gluten content. “Gluten-free” is a voluntary claim that can be used by food manufacturers on food labels if they meet all the requirements of the regulations.
On August 12, 2020, the FDA issued a final rule on the gluten-free labeling of fermented or hydrolyzed foods. It covers foods such as yogurt, sauerkraut, pickles, cheese, green olives, FDA-regulated beers and wines (e.g., generally those with less than 7 percent alcohol), and hydrolyzed plant proteins used to improve flavor or texture in processed foods such as soups, sauces, and seasonings. The rule does not change the definition of “gluten-free” but establishes compliance requirements for these hydrolyzed and fermented foods. It also includes a discussion of how FDA will verify compliance for distilled foods such as vinegar.
For more information and guidance, please check https://www.fda.gov/food/food-labeling-nutrition/gluten-free-labeling-foods.
On August 12, 2020, the FDA issued a final rule on the gluten-free labeling of fermented or hydrolyzed foods. It covers foods such as yogurt, sauerkraut, pickles, cheese, green olives, FDA-regulated beers and wines (e.g., generally those with less than 7 percent alcohol), and hydrolyzed plant proteins used to improve flavor or texture in processed foods such as soups, sauces, and seasonings. The rule does not change the definition of “gluten-free” but establishes compliance requirements for these hydrolyzed and fermented foods. It also includes a discussion of how FDA will verify compliance for distilled foods such as vinegar.
For more information and guidance, please check https://www.fda.gov/food/food-labeling-nutrition/gluten-free-labeling-foods.
Ethnic Certification
Islamic dietary laws (Halal) propose specific restrictions on diets. If you want to focus on the Islamic ethnic niche markets, consider implementing Halal certification schemes.

Vegan Certification
The Vegan has not been formally defined by the FDA, USDA or any other official U.S. agency. However, the vegan community has clearly defined and explained the term, which means a product that doesn’t include any ingredients of animal origin, including milk, eggs, honey, gelatin, meat, poultry and fish . There are multiple certification programs that help you gain the consumer trust such as Vegan.org in the U.S.
https://vegan.org/certification/
https://vegan.org/certification/



Which Quality Support Organizations in Lebanon Can Help Me?
The Lebanese Agricultural Research Institute (LARI) is a governmental organization under the Minister of Agriculture’s supervision. The institute conducts applied and basic scientific research for the development and advancement of the agricultural sector in Lebanon. Extension services for farmers include management of soil fertility, water consumptive use, plant pest, and disease control, crop rotation, and animal disease treatment and prevention, among others.
The Lebanese Standards Institution (LIBNOR) is a public institution attached to the Ministry of Industry. It was established on July 23, 1962 by a law giving it solely the right to prepare, publish, and amend national standards, as well as to grant the Lebanese Conformity Mark NL. Lebanese standards are prepared by technical committees formed by LIBNOR, which include setting the dimensions, conventions, symbols, and the definition of products’ quality, as well as the methods of testing and analysis. They also include the codes of practice for professional and structural work.
The Industrial Research Institute (IRI) is registered as a Lebanese nonprofit institution. It provides, on an international scientific level, reliable services in testing and analysis and grants certificates of quality or conformity with standards and purchase specifications. It also provides specialized technological, management, and economic consulting services to existing industries and industrial development schemes.
The Chamber of Commerce, Industry, and Agriculture of Beirut and Mount Lebanon (CCIA-BML) is a non-profit private organization operating under Decree-Law 36/67. The Lebanese Chambers are the sole providers of consular services, including certification of origin and authentication of commercial documents. Also, the chambers conduct training, develop partnerships, and organize matchmaking events and exhibitions, among other services. The CCIA-BML operates the Lebanese Training Center, which provides managerial and technical training for Lebanese enterprises. In addition, the Chamber of Commerce, Industry, and Agriculture of Tripoli and North Lebanon provides quality control center laboratories, among other services.
The Lebanese Standards Institution (LIBNOR) is a public institution attached to the Ministry of Industry. It was established on July 23, 1962 by a law giving it solely the right to prepare, publish, and amend national standards, as well as to grant the Lebanese Conformity Mark NL. Lebanese standards are prepared by technical committees formed by LIBNOR, which include setting the dimensions, conventions, symbols, and the definition of products’ quality, as well as the methods of testing and analysis. They also include the codes of practice for professional and structural work.
The Industrial Research Institute (IRI) is registered as a Lebanese nonprofit institution. It provides, on an international scientific level, reliable services in testing and analysis and grants certificates of quality or conformity with standards and purchase specifications. It also provides specialized technological, management, and economic consulting services to existing industries and industrial development schemes.
The Chamber of Commerce, Industry, and Agriculture of Beirut and Mount Lebanon (CCIA-BML) is a non-profit private organization operating under Decree-Law 36/67. The Lebanese Chambers are the sole providers of consular services, including certification of origin and authentication of commercial documents. Also, the chambers conduct training, develop partnerships, and organize matchmaking events and exhibitions, among other services. The CCIA-BML operates the Lebanese Training Center, which provides managerial and technical training for Lebanese enterprises. In addition, the Chamber of Commerce, Industry, and Agriculture of Tripoli and North Lebanon provides quality control center laboratories, among other services.




